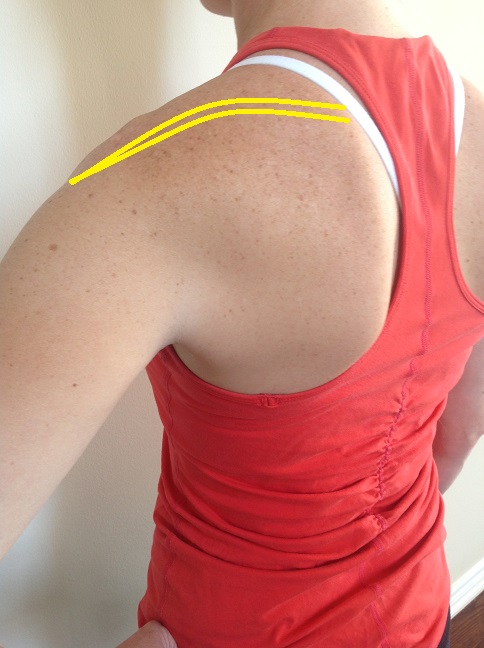
Supraspinatus Tear
The supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor and subscapularis muscles are often referred to as the rotator cuff muscles. Injury to the rotator cuff musculature is one of the more common conditions affecting the shoulder, ranging from mild strains to complete tendon rupture.
Symptoms of Supraspinatus Tear
Rotator cuff injury (including rotator cuff tear) can cause significant pain, weakness and reduced range of motion. Quite often, it causes difficulty with common daily tasks like putting your arm in a coat sleeve, putting your seat-belt on or reaching in the back seat of your car. Of course, there are many different conditions affecting the shoulder that can make these daily activities difficult and painful, so it is important to have this condition properly diagnosed.
Diagnosing Shoulder Pain
Soft tissue imaging (like diagnostic ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging) is the optimal way to diagnose rotator cuff tears. Unfortunately, there is often a waiting list for these diagnostic tests so the preliminary diagnosis is made clinically in your health practitioner’s office. This is not always a simple step, since the commonly used clinical tests are not always easy to interpret. According to the scientific literature, there does not seem to be a reliable correlation between symptoms and tearing of the rotator cuff muscles. In other words, studies have found that many patients with minimal pain and normal function of the shoulder often have imaging results indicating partial thickness tear of the supraspinatus or full thickness tear of the supraspinatus.
Rotator Cuff Treatment
Consulting with a knowledgeable and skillful diagnostician can eliminate wasted time by deciphering which tissue is likely damaged and focusing treatment on the appropriate structures as quickly as possible. That’s the first step as it helps to determine what avenue of treatment is best. For some, surgery is necessary. For most, conservative treatment like physiotherapy or chiropractic is the best choice. What is right for you? There are many factors to consider and we can assist you with that process. For example, a recent injury might benefit from laser therapy or gentle exercises with our physiotherapist. For others with more chronic rotator cuff injury (like supraspinatus tendinosis or tendinopathy) active release or graston technique with one of our chiropractors would be the best treatment. Unsure? Give us a call or send us an email…we can help you! 905.220.7858 email – [email protected]
References
Ainsworth R, Lewis JS. Exercise therapy for the conservative management of full thickness tears of the rotator cuff: a systematic review. British Journal of Sports Medicine 2007; 41: 200-210.
Uhthoff HK, Sarkar K. An algorithm for shoulder pain caused by soft-tissue disorders. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1990; 254: 121-127.
Frost P, Andersen JH et al. Is supraspinatus pathology as defined by magnetic resonance imaging associated with clinical sign of shoulder impingement? Journal Shoulder Elbow Surgery 1999; 8(6): 565-568.
Schibany N, Zehetgruber H, Kainberger F et al. Rotator cuff tears in asymptomatic individuals: a clinical and ultrasonographic screening study. Eur J. Radiol; 2004; 51(3): 263-268.
Disclaimer https://burlingtonsportstherapy.com/blog/disclaimer/